Blockchain technology is at a pivotal moment, with the demands of real-world applications outpacing the capabilities of traditional, monolithic networks. As decentralized finance, gaming, and enterprise use cases push for higher throughput and lower latency, scalability is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity. Enter data availability sampling (DAS), an innovation at the heart of modular blockchain architectures like Celestia and Avail. DAS is reshaping how blockchains handle data, opening doors to unprecedented scalability while preserving security and decentralization.

Why Data Availability Is Central to Blockchain Scalability
To understand why DAS matters, let’s revisit a core challenge: ensuring that all transaction data in a block is actually available to network participants. In monolithic blockchains like Ethereum or Bitcoin, every node must download and validate every byte of every block. This approach guarantees security but quickly runs into bottlenecks – as usage grows, so do storage and bandwidth requirements for each node. The result? Network participation narrows to only those who can afford robust hardware setups.
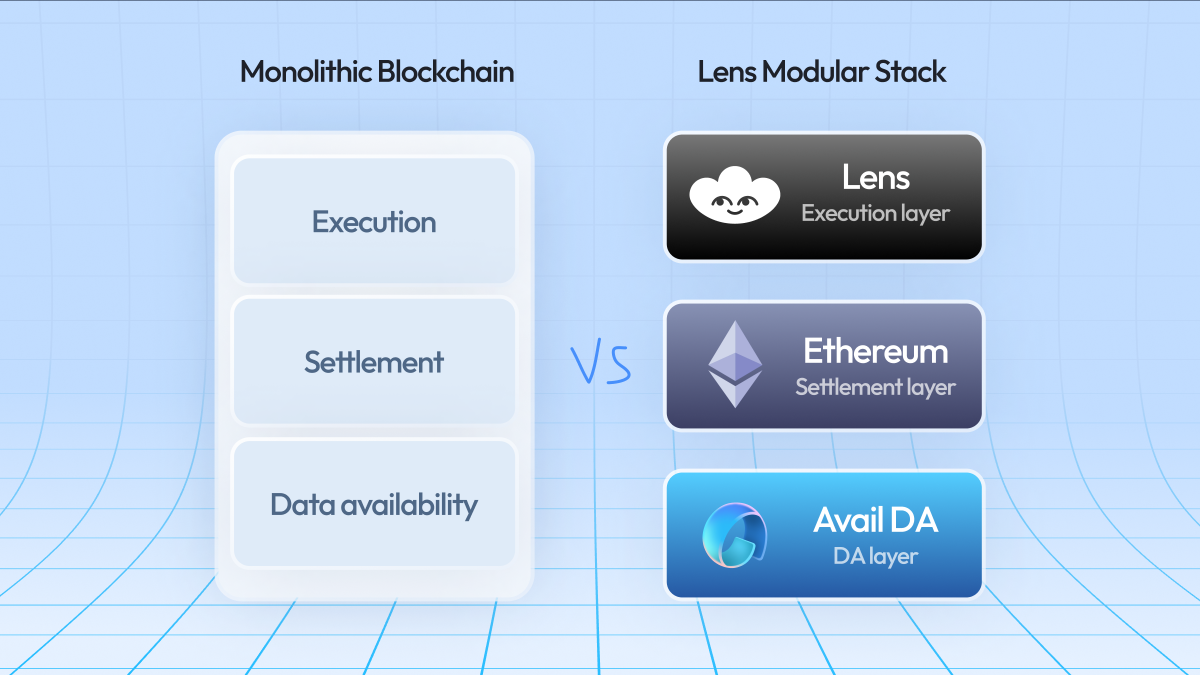
Modular blockchains flip this paradigm by splitting core functions into specialized layers: execution, consensus, and data availability. This separation allows each layer to be optimized independently for its role. The data availability layer, in particular, ensures that transaction data can be accessed by anyone who wants to verify it – but without forcing every node to store everything.
The Mechanics of Data Availability Sampling (DAS)
DAS introduces an elegant solution: instead of requiring all nodes to download entire blocks, light clients sample small random portions of each block’s data. If these samples are consistently available from the network, nodes can infer with extremely high probability that the whole block’s data is accessible.
Key Benefits of Data Availability Sampling (DAS)
-

Significantly enhances scalability by allowing nodes to verify data availability without downloading entire blocks, enabling modular blockchains like Celestia to support much larger block sizes and higher throughput.
-
Reduces bandwidth and storage requirements for individual nodes, making it feasible for light clients and mobile devices to participate in data validation without sacrificing security or decentralization.
-

Enables greater network participation by lowering hardware barriers, allowing a broader range of users and devices to contribute to network security and consensus.
-
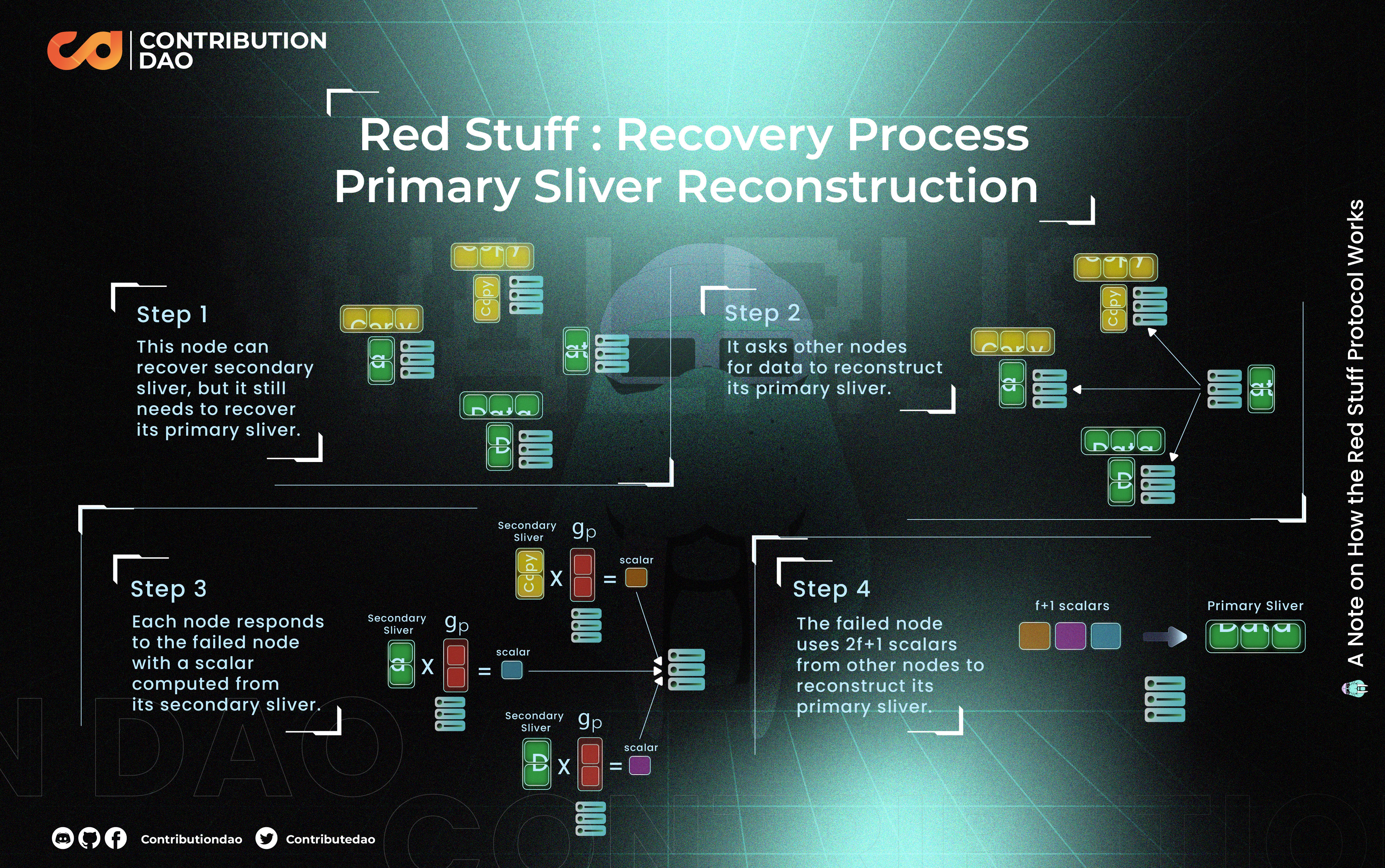
Improves data integrity and resilience through integration with erasure coding techniques, such as 2D Reed-Solomon coding in Celestia and Kate commitments in Avail, ensuring data can be reconstructed even if parts are missing.
-
Supports modular blockchain architecture by separating data availability from execution and consensus, allowing each layer to be optimized independently for flexibility, efficiency, and future upgrades.
This approach dramatically reduces bandwidth and storage requirements per node. For example, in the Celestia ecosystem, light clients use specialized software (Celestia-Node) to connect with full nodes and perform DAS. Likewise, Avail employs Fishermen nodes that actively hunt for missing or unavailable data segments on behalf of users.
This not only democratizes participation – allowing even mobile devices to validate blocks securely – but also enables networks to safely increase their block sizes without compromising on decentralization or trust-minimization.
“Data availability sampling allows light clients to verify massive blocks with minimal resources. “
DAS and Erasure Coding: A Powerful Combination
DAS reaches its full potential when combined with erasure coding techniques like 2D Reed-Solomon codes or Kate commitments. These methods encode original transaction data with redundancy so that even if some parts are missing or withheld by malicious actors, the entire dataset can be reconstructed from what remains available.
In practice, this means that even if certain validators attempt censorship by withholding specific chunks of data, honest nodes can still recover the complete information set as long as enough fragments are publicly accessible. This synergy between sampling and erasure coding underpins the robust scalability seen in leading modular DA solutions today.
A New Era for Blockchain Participation
The implications are profound: thanks to DAS, running a secure node no longer requires enterprise-grade infrastructure. Anyone with an internet connection can help secure the network and verify chain integrity – a leap forward for decentralization and resilience.
As modular blockchains like Celestia and Avail continue to innovate, data availability sampling (DAS) is proving to be a cornerstone for both scalability and inclusivity. By reducing the technical burden on individual nodes, DAS allows for a far more diverse set of participants. This diversity not only strengthens network security but also aligns with the original ethos of blockchain: open, permissionless access for all.
Consider the real-world impact: in networks leveraging DAS, validators and light clients can confidently verify blocks without running into prohibitive hardware or bandwidth costs. This means that as demand for decentralized applications grows, be it in DeFi, gaming, or supply chain, the underlying infrastructure can scale seamlessly to accommodate millions of users worldwide.
How DAS Empowers Modular Blockchain Ecosystems
The adoption of DAS is already reshaping the landscape of blockchain modularity. Projects like Celestia have demonstrated that by decoupling data availability from consensus and execution, each layer can evolve independently, integrating best-in-class innovations without being held back by legacy constraints. For example, Celestia’s use of 2D Reed-Solomon erasure coding ensures that even if a portion of block data is lost or withheld, honest nodes can reconstruct the original dataset, preserving both liveness and safety.
Meanwhile, Avail takes this further by combining DAS with Fishermen nodes, specialized actors tasked with monitoring and reporting on data gaps. This dual-layered approach not only incentivizes honest behavior but also makes it nearly impossible for malicious actors to censor or hide critical transaction data.
The result? Networks that are both scalable and robust against attacks, capable of supporting high-throughput applications without sacrificing decentralization. As more chains adopt modular architectures and integrate advanced DAS techniques, we’re witnessing the rise of a new generation of blockchains purpose-built for mass adoption.
Challenges Ahead and The Road to Widespread Adoption
No breakthrough comes without its hurdles. While DAS dramatically lowers barriers to participation, it also introduces new complexities in protocol design and implementation. Ensuring interoperability between different DA layers, and maintaining seamless user experiences as block sizes grow, remains an active area of research.
Additionally, as more projects experiment with unique combinations of erasure coding schemes and sampling algorithms, standardization will be key to ensuring security guarantees are met across diverse ecosystems. The ongoing work from teams at Celestia Labs, Avail, and others highlights the collaborative spirit driving modular blockchain innovation forward.
Leading Modular Blockchains Using Data Availability Sampling
-
Celestia is the first modular blockchain network to pioneer data availability sampling (DAS) at scale. By separating consensus and data availability, Celestia enables light nodes to efficiently verify block data through random sampling, dramatically improving scalability and decentralization. Celestia further enhances data integrity using 2D Reed-Solomon erasure coding.
-
Avail is a modular data availability layer designed for scalable blockchain ecosystems. Avail employs data availability sampling alongside erasure coding and Kate commitments (polynomial-based proofs) to ensure data integrity and accessibility. Avail’s architecture includes specialized Fishermen nodes that monitor and challenge potential data gaps, strengthening network reliability.
-

EigenDA (by EigenLayer) is an innovative data availability solution built on Ethereum, leveraging data availability sampling and restaking to provide scalable, decentralized data availability for rollups and modular chains. EigenDA enables rollups to post data securely and cost-effectively, supporting Ethereum’s modular future.
-
Polygon Avail (formerly known as Polygon Avail) is a specialized data availability blockchain developed by Polygon Labs. It utilizes data availability sampling and erasure coding to provide scalable, modular data availability for Layer 2 solutions and rollups, enabling efficient light client verification and supporting the broader Polygon ecosystem.
The excitement around modular architectures isn’t just theoretical, it’s backed by a vibrant developer community building practical solutions today. Whether you’re an app developer seeking scalable infrastructure or a researcher exploring new cryptographic primitives, now is the time to engage with this rapidly evolving space.
“DAS doesn’t just make blockchains faster, it makes them fairer. “
If you’re interested in diving deeper into how these systems work under the hood or want to stay updated on breakthroughs as they happen, explore resources like this comprehensive guide on modular DA layers. The future of blockchain scalability isn’t just about bigger blocks, it’s about smarter architecture choices that empower everyone to participate securely at scale.






