Blockchain networks have long faced a core dilemma: how can they scale to accommodate millions of users while staying decentralized and secure? At the heart of this challenge lies the concept of data availability. For a blockchain to function trustlessly, every participant must be able to verify that all transaction data is accessible and unaltered. Enter Data Availability Sampling (DAS), an elegant solution that is rapidly transforming modular blockchain architectures.

Why Data Availability Matters in Modular Blockchains
The rise of modular blockchains like Celestia and EigenDA has shifted the focus from monolithic chains (where consensus, execution, and data storage are bundled together) to specialized layers. In this landscape, the data availability layer guarantees that raw transaction data is truly accessible to the network. If even a small portion of block data goes missing or becomes unavailable, it undermines the entire premise of decentralized verification.
This is where DAS blockchain technology shines. Instead of requiring every node to download massive blocks in their entirety, DAS empowers lightweight clients – often called light nodes – to participate in decentralized verification. This lowers hardware barriers and increases network resilience by enabling more diverse participants.
The Mechanics: How Data Availability Sampling Works
DAS leverages two key innovations: erasure coding and random sampling. When a block producer creates a new block, it divides the data into many small segments and applies erasure coding. This process adds redundancy so that even if parts are missing, the original dataset can still be reconstructed. Light clients then randomly sample small pieces from across these segments.
Key Benefits of DAS for Blockchain Scalability
-
Enables Lightweight Verification for Nodes: Data Availability Sampling (DAS) allows light clients to securely verify data availability without downloading entire blocks, reducing bandwidth and storage requirements for participants.
-
Boosts Network Throughput and Scalability: By minimizing the data each node must process, DAS supports higher transaction throughput and larger block sizes, paving the way for scalable blockchain solutions.
-

Promotes Greater Decentralization: DAS empowers resource-constrained devices to participate in network verification, leading to a more decentralized and inclusive blockchain ecosystem.
-
Reduces Reliance on Trusted Entities: With probabilistic, trust-minimized verification, DAS allows nodes to independently confirm data availability, strengthening the trustless nature of blockchains.
-
Facilitates Modular Blockchain Architectures: DAS underpins the design of modular blockchains like Celestia, enabling separation of consensus and data availability layers for flexible, scalable networks.
If enough randomly selected samples are available and verifiable, it becomes statistically improbable that any data is missing or withheld by malicious actors. The more samples checked successfully, the higher the confidence in full data availability – all without forcing every node to store or process entire blocks.
DAS in Action: Celestia and Ethereum’s Roadmap
Celestia DAS stands as one of the most prominent real-world implementations. By using DAS, Celestia enables light nodes with minimal hardware requirements to help secure the network while supporting much larger block sizes than traditional blockchains can safely handle. This breakthrough means rollups and other layer-2 solutions can anchor their data on Celestia’s DA layer without sacrificing decentralization or throughput.
The Ethereum ecosystem is also embracing DAS as part of its ongoing scalability roadmap, especially as sharding matures and rollups proliferate. By integrating probabilistic sampling into its protocol design, Ethereum aims to ensure robust modular blockchain data availability for years to come.
The Probabilistic Power Behind Decentralized Verification
The beauty of DAS lies in its probabilistic guarantees. Unlike traditional systems where verification means total duplication (and thus high cost), DAS lets resource-constrained devices meaningfully contribute to security by only checking tiny slices at random intervals. Over time and across thousands of participants, this forms a robust web of checks that makes censorship or hidden data nearly impossible.
This shift to probabilistic, lightweight verification is more than a technical optimization, it’s a philosophical evolution for blockchains. By lowering the hardware requirements for participation, data availability sampling (DAS) democratizes network access and strengthens decentralization. It invites a broader spectrum of validators and users to join, ensuring that blockchains remain open and resilient as they scale.
Real-World Impact: Scaling Without Sacrificing Security
The impact of DAS is already evident in projects like Celestia and the emerging EigenDA ecosystem. Celestia’s implementation allows rollups to post larger blocks, increasing transaction throughput while maintaining robust decentralized verification. This unlocks new possibilities for decentralized applications, from high-frequency trading platforms to complex gaming worlds, all without centralizing risk or trust.
Ethereum’s plans to weave DAS into its sharding architecture signal a major leap forward. As rollups become the dominant scaling solution, ensuring reliable data availability is critical. DAS enables Ethereum to support massive user growth while keeping the network secure, without forcing every participant to run heavyweight infrastructure.
Key Advantages at a Glance
How DAS Boosts Blockchain Decentralization & Efficiency
-
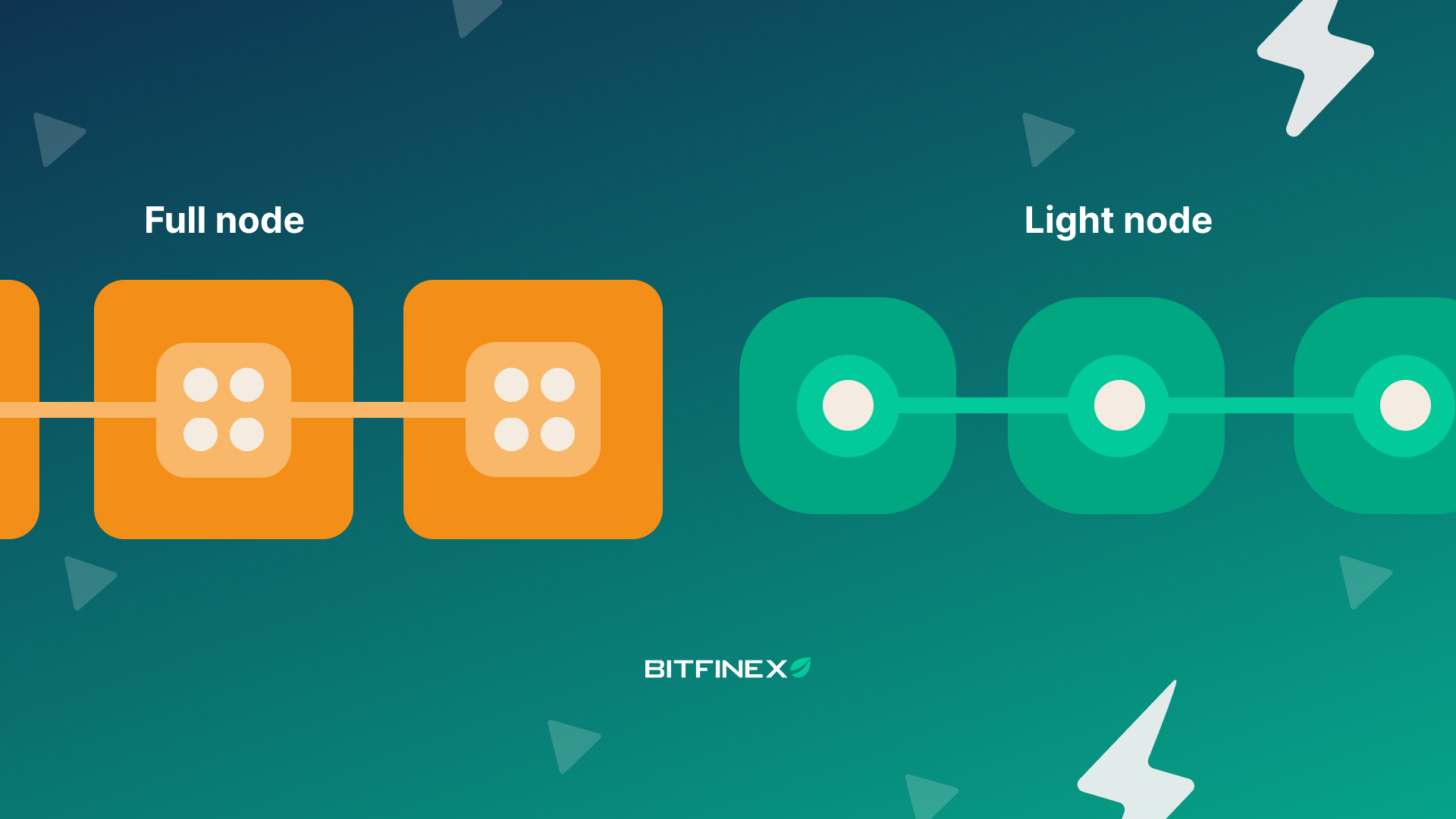
Enables Lightweight Verification by Light Nodes: Data Availability Sampling (DAS) allows light clients to verify data availability without downloading entire blocks, making it possible for more participants to join the network with minimal hardware.
-
Reduces Barriers for Decentralized Participation: By lowering computational and storage requirements, DAS empowers resource-constrained devices—like smartphones and IoT devices—to help secure and verify the blockchain, increasing overall decentralization.
-

Improves Network Scalability: DAS enables blockchains to increase transaction throughput by allowing nodes to process less data per block, paving the way for larger block sizes and more efficient scaling solutions.
-
Supports Trust-Minimized Verification: With DAS, nodes can independently and probabilistically confirm that all transaction data is available, reducing reliance on trusted third parties and enhancing the trustless nature of blockchain networks.
-

Powers Modular Blockchain Architectures: Platforms like Celestia utilize DAS to separate consensus from data availability, allowing for more flexible and efficient blockchain designs that can adapt to various use cases.
-

Enables Scalable Rollups and Sharding: DAS is a key component in the scalability roadmaps of major blockchains like Ethereum, supporting technologies such as rollups and sharding by ensuring data is available without overburdening nodes.
For developers and researchers, these advances mean new design patterns are possible. Decentralized applications can now rely on modular DA layers for efficient data storage and retrieval, opening the door to innovative use cases that were previously bottlenecked by bandwidth or storage constraints.
What’s Next for Data Availability Sampling?
The future of DAS blockchain technology looks bright. As more networks adopt modular architectures and experiment with advanced erasure coding techniques, we can expect even greater improvements in scalability and security. Projects like EigenDA are pushing the limits further by optimizing sampling algorithms and exploring new cryptographic primitives tailored for fast verification.
Community engagement is also key. With DAS making it possible for anyone with a smartphone or laptop to participate in decentralized verification, education around best practices and security assumptions becomes crucial. The next wave of innovation will likely come from grassroots contributors leveraging these lightweight tools in creative ways.
“DAS represents a foundational shift, moving us from heavy, resource-intensive consensus towards agile, inclusive participation. “
How likely are you to run a light node on a modular data availability (DA) layer in 2025?
With Data Availability Sampling (DAS) making it easier for resource-constrained devices to help secure blockchains, running a light node is more accessible than ever. Would you consider participating in a modular DA network like Celestia next year?
Getting Involved: Resources and Further Learning
If you’re eager to dive deeper into data availability sampling or want hands-on experience running light nodes, start by exploring resources from leading projects:
Stay tuned as this space evolves rapidly, modular blockchain data availability isn’t just an upgrade; it’s reshaping what trustless systems can achieve at global scale.






