For years, blockchain’s promise of open, decentralized systems has been hampered by an unforgiving trade-off: as networks scale to serve millions, decentralization and security are often the first casualties. In 2025, data availability layers (DALs) have moved from technical curiosity to critical infrastructure, underpinning the next generation of scalable, permissionless blockchains. By decoupling data storage and propagation from execution and consensus, DALs enable blockchains to process thousands of transactions per second without centralizing trust or inflating node requirements.

Why Data Availability Matters for Blockchain Scaling
At its core, data availability means that every participant in a network can access all the information necessary to verify new blocks. In traditional monolithic blockchains like early Ethereum or Bitcoin, execution, consensus, and data storage are bundled together. This design ensures strong security but limits throughput: every full node must download and store all transaction data. As a result, the more users join and transact on these networks, the greater the burden on individual nodes, leading either to higher costs or creeping centralization.
Data availability layers flip this paradigm. By offloading data storage and propagation to specialized layers, separate from execution and consensus, blockchains can scale horizontally. This modular approach allows networks to support lighter nodes that don’t need to store every byte of historical data but can still independently verify state transitions. The outcome is higher throughput and lower fees without ceding control to a handful of powerful validators.
The Anatomy of Modular Blockchain Architecture in 2025
The rise of DALs is inseparable from the modular blockchain movement. In this architecture:
- Execution Layers handle transaction processing and state updates.
- Consensus Layers ensure global agreement about transaction order and validity.
- Data Availability Layers guarantee that all transaction data is published in a way that anyone can retrieve and verify it.
This separation allows each layer to specialize. For example, Celestia pioneered standalone DALs that offer verifiable data publication without running their own smart contracts or consensus engines. Ethereum’s roadmap now prioritizes danksharding, where data blobs are posted directly on-chain for rollups to use, enabling over 100,000 transactions per second while keeping node requirements manageable.
Techniques That Power Modern Data Availability Layers
Diving deeper into how DALs work reveals several sophisticated mechanisms designed for efficiency:
- Data Availability Sampling (DAS): Rather than downloading entire blocks, nodes randomly sample small pieces of each block’s data. If enough samples are validly available across the network, participants can be confident the whole block is accessible, minimizing bandwidth while maximizing trustlessness.
- Erasure Coding: By encoding redundancy directly into published data (think digital error-correcting codes), DALs ensure that even if parts of a dataset go missing or are withheld by malicious actors, honest nodes can reconstruct the original information from fragments.
- On-chain vs Off-chain Storage: Some DA solutions keep all data on-chain for maximum security but limited scalability; others use off-chain networks with cryptographic proofs for greater throughput at the cost of more complex trust assumptions.
This technical evolution has real-world consequences: projects like NEAR Protocol use sharding plus stateless validation to distribute both computation and storage across many nodes; Celestia acts as a universal DA backbone for sovereign rollups; Ethereum’s danksharding roadmap aims to make high-throughput applications possible without sacrificing decentralization or self-custody.
The Market Impact: Lower Fees Without Centralizing Power
The practical upshot? Data availability layers have become foundational for reducing blockchain fees while preserving permissionless access. As rollups proliferate atop robust DALs in 2025, from DeFi protocols with global reach to Web3 games demanding instant settlement, the bottleneck is no longer how much computation a single chain can handle but how efficiently it can publish and propagate raw transactional data across thousands or millions of lightweight verifiers worldwide.
What this means for users is simple but profound: lower transaction costs and a more inclusive network, without the creeping centralization that plagued previous scaling experiments. The days when high fees priced out everyday users or forced projects onto less secure sidechains are receding, replaced by a landscape where data propagation is distributed and verifiable at scale. The modular approach ensures that no single entity can throttle access to data or unilaterally dictate the terms of participation.
Real-World Use Cases of Data Availability Layers in Web3
-
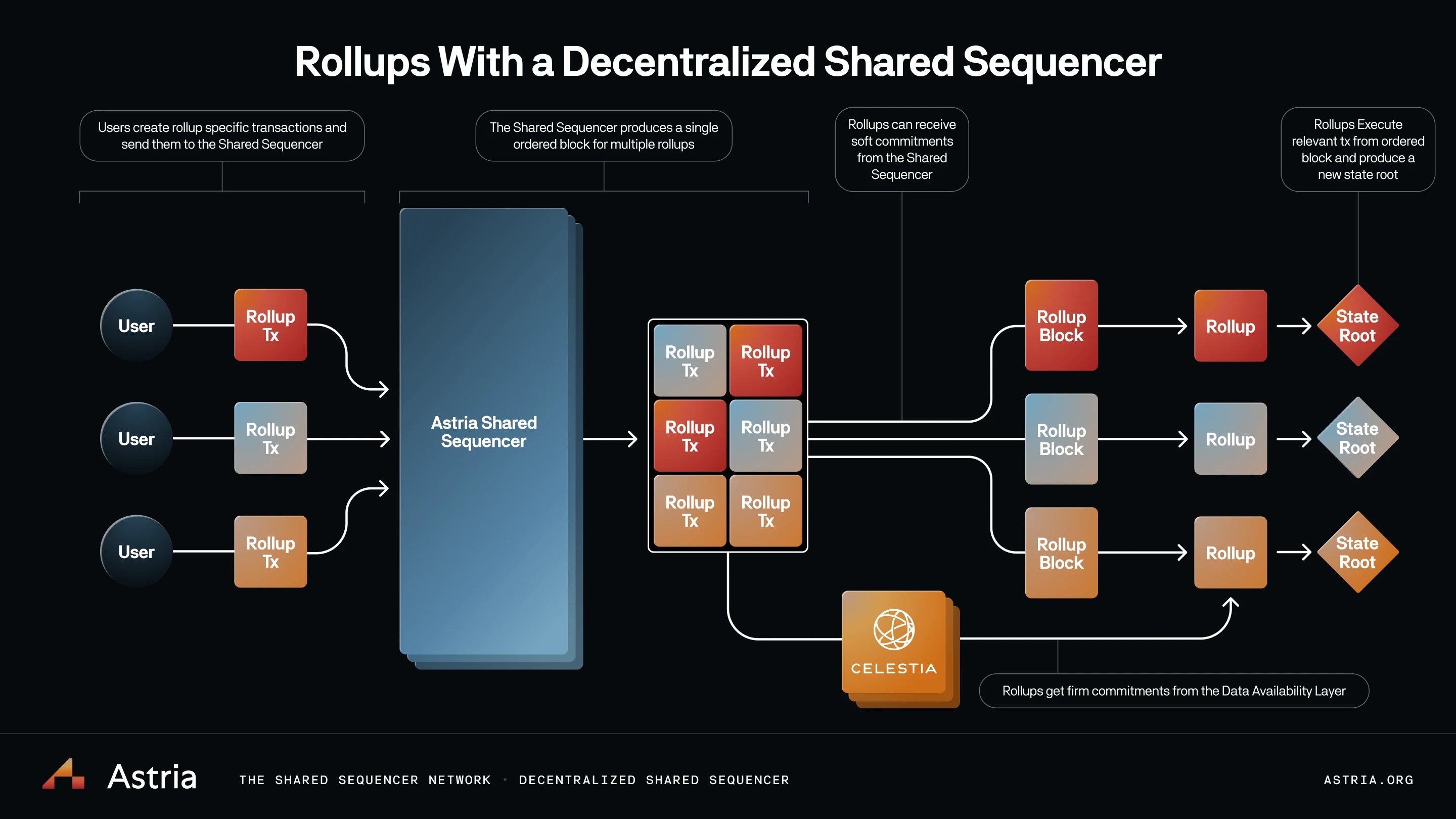
Celestia powering DeFi rollups: Celestia serves as a modular data availability layer for DeFi-focused rollups like Rollkit and Optimism, enabling high-throughput decentralized exchanges and lending platforms without compromising security or decentralization.
-
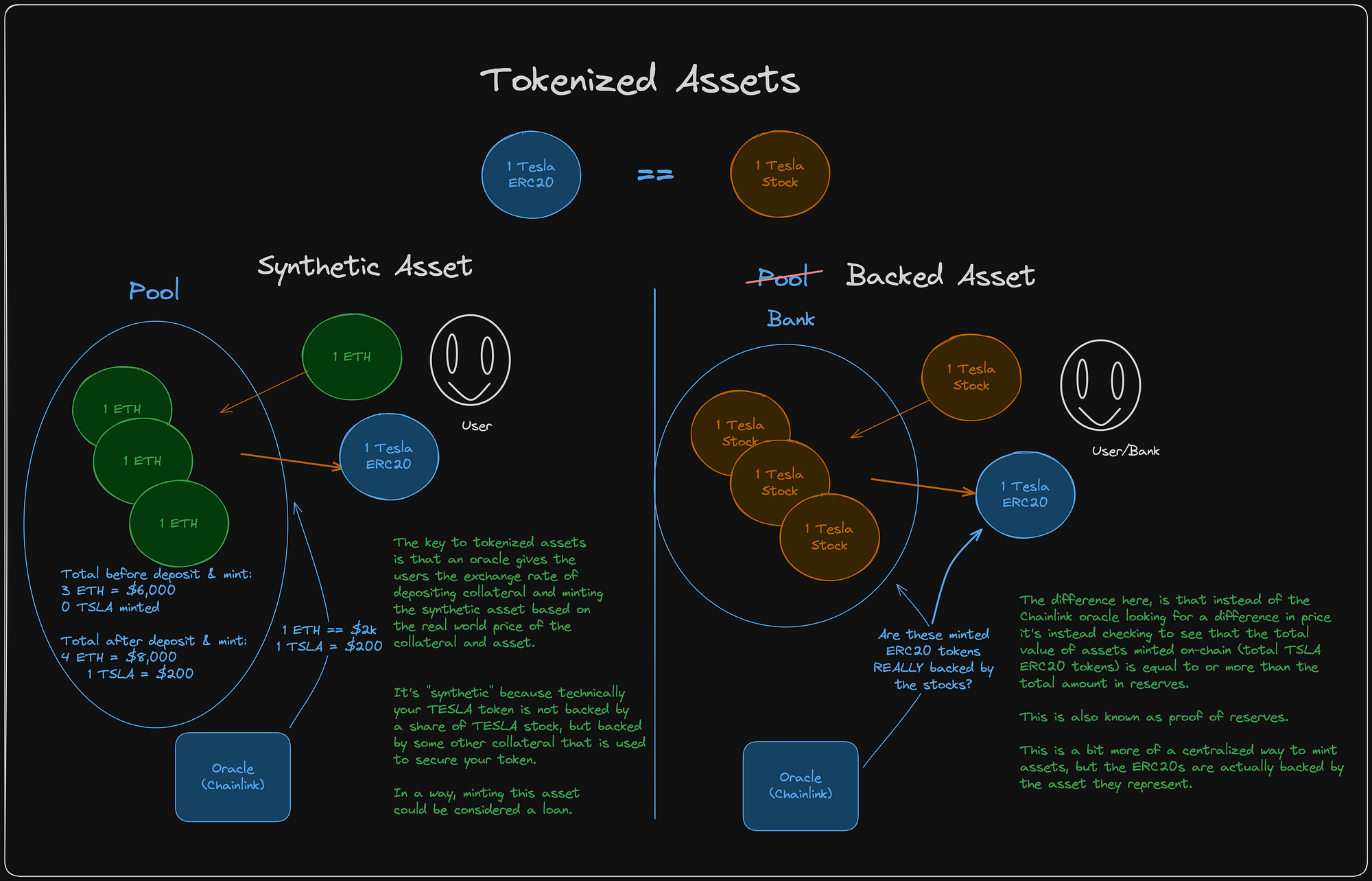
Ethereum Danksharding for scalable DeFi and tokenized assets: The introduction of Danksharding and data blobs on Ethereum allows DeFi protocols and tokenized real-world asset platforms to process massive volumes of transactions efficiently, supporting innovations like on-chain bonds and stablecoins.
-

NEAR Protocol’s sharded gaming ecosystems: NEAR Protocol leverages its data availability solution and sharding to support large-scale blockchain gaming platforms, enabling fast, low-cost in-game asset transfers and NFT minting while maintaining decentralization.
-

Polygon Avail for cross-chain tokenized assets: Polygon Avail acts as a data availability layer for multi-chain applications, facilitating seamless transfer and verification of tokenized assets across different blockchains, critical for interoperable DeFi and asset markets.
-
Starknet’s DA integration for high-performance gaming and DeFi: Starknet utilizes external data availability layers to boost transaction throughput for decentralized gaming and DeFi dApps, ensuring data is always accessible and verifiable by all participants.
For developers, DALs have unlocked new design space. Instead of working around monolithic bottlenecks, teams can launch custom execution environments, rollups or appchains, anchored by robust data availability guarantees. This flexibility has spurred an explosion of experimentation in both consumer-facing and institutional-grade blockchain applications. Critically, as more blockchains adopt modular DA strategies, composability between ecosystems improves: rollups on different chains can interoperate more easily when they share a common data backbone.
Risks and Open Questions for 2025
Yet the move to modularity is not without trade-offs. Security and incentive design remain live concerns. Off-chain data availability introduces new attack surfaces, if too few nodes participate or economic incentives falter, liveness guarantees could be undermined. There are also open questions about how to best align rewards for data propagators with network security, especially as competition among DA providers heats up.
The threat of re-centralization also looms if a handful of large operators dominate DA services. To mitigate this risk, leading protocols are experimenting with permissionless node onboarding and cryptographic proofs that minimize trust assumptions. The goal is clear: ensure that anyone can verify the full dataset independently, regardless of their hardware or geographic location.
Strategic Outlook: Where Data Availability Layers Go Next
The next phase will be defined by interoperability and vertical specialization. As DALs mature, expect to see tailored solutions for specific sectors, high-frequency trading platforms may demand ultra-low latency DA layers; NFT marketplaces might prioritize long-term archival storage; global payment rails could seek hybrid on/off-chain architectures tuned for compliance.
This evolution positions DALs not just as scalability tools but as strategic infrastructure underpinning Web3’s most ambitious use cases. Their continued adoption will determine whether blockchain technology finally achieves mainstream parity with Web2 systems in terms of cost, speed, and reliability, without abandoning its foundational ethos of decentralization.
If you’re building in this ecosystem or evaluating blockchain scalability solutions for your organization’s next move, understanding the nuances of modern DA layers is essential. For deeper technical dives into how these systems work under the hood, and what trade-offs come with each model, explore our resource on modular blockchains and their future directions.






