Blockchain scalability has always been a delicate balancing act. In 2025, the emergence of modular blockchain architectures has fundamentally altered the landscape, with data availability layers (DALs) at the center of this transformation. By decoupling execution, consensus, and data storage into specialized layers, modular blockchains are now able to process orders of magnitude more transactions while preserving decentralization and security.

The Role of Data Availability Layers in Modular Blockchain Design
Traditional monolithic blockchains like early Ethereum or Bitcoin handled all core functions, transaction execution, consensus, and data storage, on a single chain. This architecture limited throughput due to bottlenecks in how much data nodes could process and store. Enter the modular approach: by separating these concerns, each layer can optimize for its unique function. Data availability layers are responsible for ensuring that all transaction data is reliably stored and accessible to network participants for verification.
This separation means that DALs act as the backbone for scalable blockchains. They provide a trustless environment where anyone can verify that transaction data is available before it is finalized on-chain. As noted by Celestia and other leading projects, this enables networks to scale without sacrificing decentralization, a critical trade-off in previous designs. For a deeper technical dive on how DALs solve scalability bottlenecks without undermining decentralization, see our in-depth guide.
How Data Availability Layers Enable Massive Transaction Throughput
The most significant impact of DALs is their ability to offload vast amounts of transaction data from the main chain. Instead of requiring every node to store all historical data forever, a major constraint in monolithic chains, DALs allow nodes to verify data availability without holding it indefinitely. This unlocks new scaling techniques like sharding and rollups.
Ethereum’s 2025 upgrades, including Danksharding and Verkle Trees, illustrate this evolution perfectly. By introducing “data blobs” that are posted to dedicated DALs rather than clogging up mainnet storage, Ethereum now processes over 100,000 transactions per second with dramatically reduced gas fees. Meanwhile, rollups like Optimism and Arbitrum leverage DALs for posting compressed transaction proofs off-chain while relying on the shared security of Ethereum’s settlement layer.
This paradigm shift isn’t limited to Ethereum. NEAR Protocol’s dynamic resharding mechanism allows the network to adjust shard count in real time based on demand, scaling from 8 to 9 shards with zero downtime in August 2025 and achieving a 12.5% throughput boost instantly.
Key Benefits Driving Adoption in 2025
Top Benefits of Modular Data Availability Layers in 2025
-

Massive Scalability: Modular DA layers like Celestia and Ethereum Danksharding enable blockchains to process 100,000+ transactions per second by offloading data storage, eliminating congestion and unlocking unprecedented throughput.
-
Significant Cost Reduction: By optimizing how data is stored and accessed, solutions such as NEAR Protocol’s DA layer and Verkle Trees dramatically lower transaction fees, making decentralized applications more affordable for users and developers.
-
Enhanced Security & Decentralization: DALs ensure transaction data is readily available for all network participants, supporting trustless verification and preserving the decentralized ethos of blockchains. Projects like EigenDA provide robust, decentralized data storage for rollups.
-
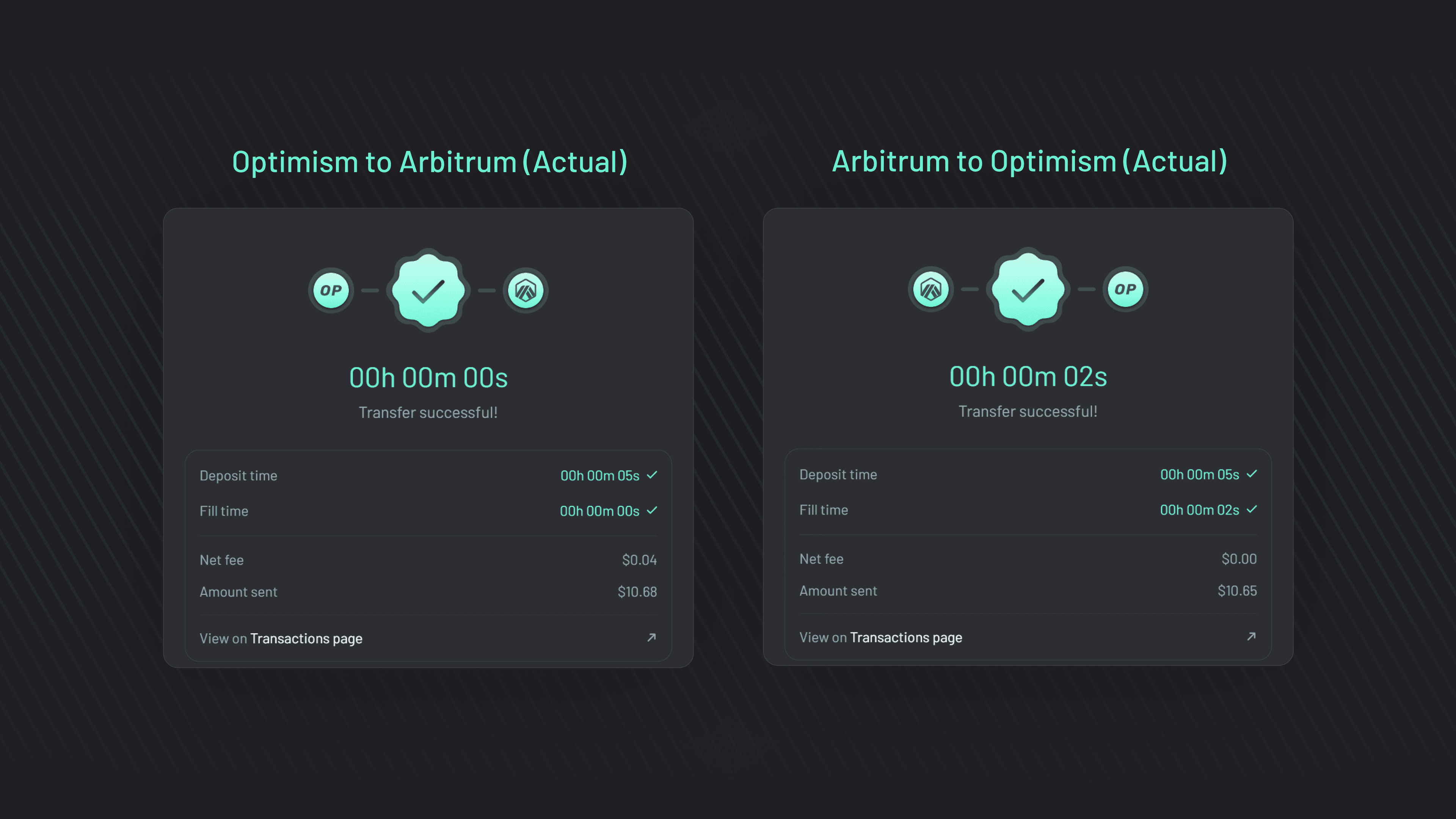
Seamless Rollup Integration: Data availability layers are pivotal for rollups such as Optimism and Arbitrum, providing reliable storage for off-chain execution data and enabling scalable, secure Layer 2 solutions.
-
Flexible and Modular Upgrades: Specialized DA layers allow independent upgrades and innovations. For example, dynamic resharding in NEAR Protocol lets the network scale resources on demand without downtime, boosting adaptability.
The adoption curve for data availability solutions is steep because these layers enable:
- Unprecedented Scalability: Transaction throughput increases exponentially as storage bottlenecks are removed.
- Cost Efficiency: Transaction fees plummet as optimized storage reduces resource requirements across the stack.
- Decentralization and Security: Trustless verification ensures no single party controls access or validity of transaction data.
- Ecosystem Flexibility: Independent upgrades at each layer foster rapid innovation without risking network stability.
This synergy between specialized layers allows networks like Celestia DA and EigenDA to offer customizable solutions tailored for different Layer 2 protocols or decentralized applications (dApps). For more detail on how such architecture enables parallel execution and scalable dApps, check out our analysis on parallel execution via DA layers.
As modular blockchains mature, the integration of DA layers is reshaping the way developers and users engage with decentralized applications. By decoupling data storage from execution, DALs empower Layer 2 solutions, sovereign rollups, and application-specific chains to achieve both high throughput and robust security guarantees without inheriting the limitations of monolithic architectures.
Celestia DA and EigenDA have emerged as leading examples in this rapidly evolving landscape. Their interoperable data availability services allow new projects to launch with confidence that their transaction data will remain verifiable and accessible, even as transaction volumes surge. This modularity not only accelerates time-to-market for novel dApps but also reduces the technical burden on teams building next-generation financial protocols, social platforms, or gaming ecosystems.
Challenges and Ongoing Research in Data Availability Layers
No technology is without trade-offs. While DALs solve critical bottlenecks, they introduce new considerations around data sampling, erasure coding, and incentive alignment for validators. Researchers are actively exploring how to further optimize light client proofs so that even resource-constrained devices can verify data availability efficiently. Additionally, questions remain about long-term data persistence, how much historical data should be retained off-chain versus on-chain to balance efficiency with auditability?
The competitive landscape is also intensifying as more chains adopt modular designs. Projects are experimenting with hybrid models that leverage both shared DA layers (for interoperability) and dedicated solutions (for specialized use cases). For example, some gaming rollups now combine Celestia DA’s global consensus with bespoke DA layers optimized for real-time game state updates.
Real-World Impact: Lower Barriers for Developers and Users
The upshot of these advances is a dramatically lower barrier to entry for building scalable blockchain applications. Developers can now compose execution environments atop proven DA providers without reinventing core infrastructure. Users benefit from lower fees, faster settlement times, and a broader range of decentralized services unencumbered by legacy throughput ceilings.
This dynamic has led to an explosion of experimentation in consumer-facing dApps throughout 2025, ranging from decentralized finance protocols capable of microsecond settlement to NFT platforms supporting massive on-chain media files. As noted in our review of blockchain scalability bottlenecks, the modular stack’s flexibility is unlocking use cases previously thought impossible on public chains.
What’s Next? The Roadmap for Modular Blockchain Scalability
The future trajectory points toward even greater composability between execution environments and DA providers. Innovations like data availability sampling, universal light clients, and cross-layer incentive mechanisms are being deployed to ensure that performance gains do not come at the expense of decentralization or user sovereignty.
For developers evaluating their options in late 2025, the key is understanding how each layer interacts within the broader ecosystem, and where trade-offs between cost, speed, and trust assumptions align with project goals. As competition heats up among Celestia DA, EigenDA, NEAR Protocol’s native solutions, and emerging challengers, expect further reductions in transaction fees alongside continued improvements in throughput reliability.
The bottom line: Data availability layers have moved from theoretical constructs to production-grade infrastructure underpinning Web3’s most ambitious visions. Their ability to enable modular blockchain scalability marks a paradigm shift, one that will define how decentralized systems evolve well into 2026 and beyond.






